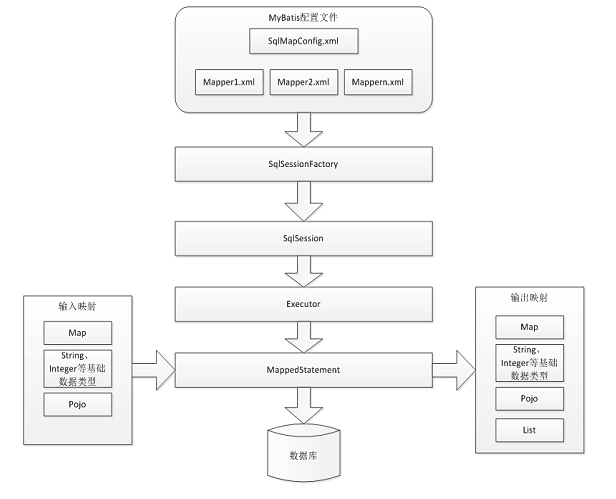
为什么要使用mybaties 由于jdbc有以下一些问题:
1、数据库连接创建、释放频繁造成系统资源浪费,从而影响系统性能。如果使用数据库连接池可解决此问题。
使用mybaties可以比较好的解决上面的问题
#####mybaties原理
mybatis配置
配置信息 mybaties的核心配置文件是sqlMapConfig.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration > <environments default ="development" > <environment id ="development" > <transactionManager type ="JDBC" /> <dataSource type ="POOLED" > <property name ="driver" value ="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name ="url" value ="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8" /> <property name ="username" value ="root" /> <property name ="password" value ="root" /> </dataSource > </environment > </environments > <mappers > <mapper resource ="sqlmap/User.xml" /> </mappers > </configuration >
所有的sql语句都写到配置文件里面去了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace ="test" > <select id ="findUserById" parameterType ="Integer" resultType ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" > select * from user where id = #{v} </select > <select id ="findUserByUserName" parameterType ="String" resultType ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" > select * from user where username like "%"#{value}"%" </select > </mapper >
测试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 package junit;import java.io.InputStream;import java.util.List;import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;import org.junit.Test;import cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User;public class MybatiesTest public void testMybaties () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById" , 10 ); System.out.println(user); } @Test public void testMybatiesByName () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); List<User> users = sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByUserName" , "王" ); for (User user : users) { System.out.println(user); } } }
注意:当返回是一个list的时候,使用selectList()方法查询,resultType表示的就是list的范型
添加用户 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <insert id ="insertUser" > <selectKey resultType ="Integer" order ="AFTER" keyProperty ="id" > select LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey > insert into user (username, birthday, sex, address) values (#{username}, #{birthday}, #{sex}, #{address}) </insert >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Test public void testInsertUser () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = new User("何炅" , "女" , new Date(), "阳光大道18号" ); int index = sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser" , user); sqlSession.commit(); System.out.println(user.getId()); }
注意:
LAST_INSERT_ID()是mysql提供的函数,表示最近增长的的数据的id,如果是mysql order要选择AFTER, oracle选择BEFORE, keyProperty表示放到对应的类的哪个属性里面
修改用户 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void UpdateUserById () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = new User(29 , "何日火" , "女" , new Date(), "阳光大道18号" ); int index = sqlSession.update("test.updateUser" , user); sqlSession.commit(); }
1 2 3 4 5 6 <update id ="updateUser" parameterType ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" > update user set username = #{username}, birthday = #{birthday}, sex = #{sex} where id = #{id} </update >
删除用户 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public void DelUserById () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUserById" , 28 ); sqlSession.commit(); }
1 2 3 4 <delete id ="deleteUserById" parameterType ="Integer" > delete from user where id = #{vvv} </delete >
mybaties和hibernate的区别 1、Mybatis和hibernate不同,它不完全是一个ORM框架,因为MyBatis需要程序员自己编写Sql语句。
2、Mybatis学习门槛低,简单易学
3、程序员直接编写原生态sql,可严格控制sql执行性能,灵活度高,非常适合对关系数据模型要求不高的软件开发,例如互联网软件、企业运营类软件等,因为这类软件需求变化频繁,但需求变化要求成果输出迅速。
4、mybatis无法做到数据库无关性,如果需要实现支持多种数据库的软件则需要自定义多套sql映射文件,工作量大。
总之,按照用户的需求在有限的资源环境下只要能做出维护性、扩展性良好的软件架构都是好架构,所以框架只有适合才是最好。
Mapper动态代理 原则:
1、Mapper.xml文件中的namespace与mapper接口的完整类路径相同。
例如:
接口
1 2 3 4 5 public interface UserMapper public User findUserById (Integer id) }
UserMapper.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace ="com.itheima.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper" > <select id ="findUserById" parameterType ="Integer" resultType ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" > select * from user where id = #{v} </select > </mapper >
测试:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Test public void testMapper () throws Exception String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml" ; InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in); SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); User user = userMapper.findUserById(10 ); System.out.println(user); }
小结:
mybatis官方推荐使用mapper代理方法开发mapper接口,程序员不用编写mapper接口实现类,使用mapper代理方法时,输入参数可以使用pojo包装对象或map对象,保证dao的通用性。
取别名 可以在sqlMapConfig.xml里面设置别名,这样写sql语句的xml文件时就不需要写完整类名了,用别名即可
1 2 3 <typeAliases > <typeAlias type ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" alias ="User" /> </typeAliases >
这是将cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User明确指定为User
1 2 3 <typeAliases > <package name ="cn.itcast.mybatis.po" /> </typeAliases >
这是指定cn.itcast.mybatis.po这个包下面所有类名,例如cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User指定为user和User,一般最好指定的包名下面都是pojo类
映射器 在mapper标签里面有三个属性,分别是resource、url、class 这三个属性只能出现一个,resource用法如下
1 2 3 <mappers > <mapper resource ="com/itheima/mybatis/mapper/UserMapper.xml" /> </mappers >
使用mapper接口类路径
1 <mapper class ="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper" />
注意:此种方法要求mapper接口名称和mapper映射文件名称相同,且放在同一个目录中。
url要用绝对路径,现在不用
使用package接口类路径
注册指定包下的所有mapper接口
1 <package name ="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper" />
注意:此种方法要求mapper接口名称和mapper映射文件名称相同,且放在同一个目录中。现在package用得多